Data is fundamentally what drives business operations; protecting this intellectual capital is essential. However, with the explosive growth of data and increasing requirements for business continuity/disaster recovery, it is becoming impractical to keep all data within the confines of privately maintained data centers. That’s why so many enterprises today are turning to the cloud, as it enables users to avoid the difficulties of setting up and maintaining a dedicated remote location.
However, the challenges associated with replicating data into the cloud can be extensive. An on-premises software-defined storage solution with disaster recovery to the cloud can significantly reduce the effort required.
Simplifying Cloud Replication with Software-Defined Storage
Data is fundamentally what drives business operations; protecting this intellectual capital is essential. However, with the explosive growth of data and increasing requirements for business continuity/disaster recovery, it is becoming impractical to keep all data within the confines of privately maintained data centers. At the same time, ease of access to business-critical data and applications is imperative. It can make the difference between emerging from a crisis at minimal cost and maximum speed, or jeopardizing a business’s reputation and bottom line.
Business continuity best practices, along with the wide variety of compliance regulations to which many organizations must adhere, require that all essential data and applications be available at a remote site—accessible from anywhere—to ensure that business operations can be restored in the event of an unforeseen event or disaster scenario. But replicating operations at a remote physical site can be expensive and difficult. That’s why so many enterprises today are turning to the cloud, as it enables users to avoid the difficulties of setting up and maintaining a dedicated remote location.
However, the challenges associated with replicating data into the cloud can be extensive. Furthermore, the tasks involved in securing the transmitted data to and from the cloud are even more arduous, because it involves the setup and configuration of a secure VPN and federation. The ever-changing data residency laws with GDPR and other compliance mandates further complicate the implementation of this already sophisticated task. Lastly, the legal requirements for encrypting data in transit add to the mounting challenges of cloud replication. An on-premises software-defined storage solution with disaster recovery to the cloud can significantly reduce the effort required.
Software-defined storage data services play an integral role in helping users to take advantage of the operational flexibility, scalability, agility and cost-efficiencies of private, public and hybrid clouds, while utilizing existing storage resources and skills. It makes it much simpler for businesses to quickly roll out a secure remote replication site to safeguard a highly available data center, while enjoying unified storage management between on-premises infrastructure and the cloud.
There are two key technologies critical to enabling this: asynchronous remote replication and snapshot clones. The first has the advantage of standing up operational elements in the cloud to ensure business continuity and replicating change data back to on-prem resources to resume business operations seamlessly. The latter is a backup/secondary storage solution that provides a low-cost alternative to on-site or tape backup with near-line characteristics. Both of these options can be configured to provide highly effective cloud-based backup solutions with software-defined storage.
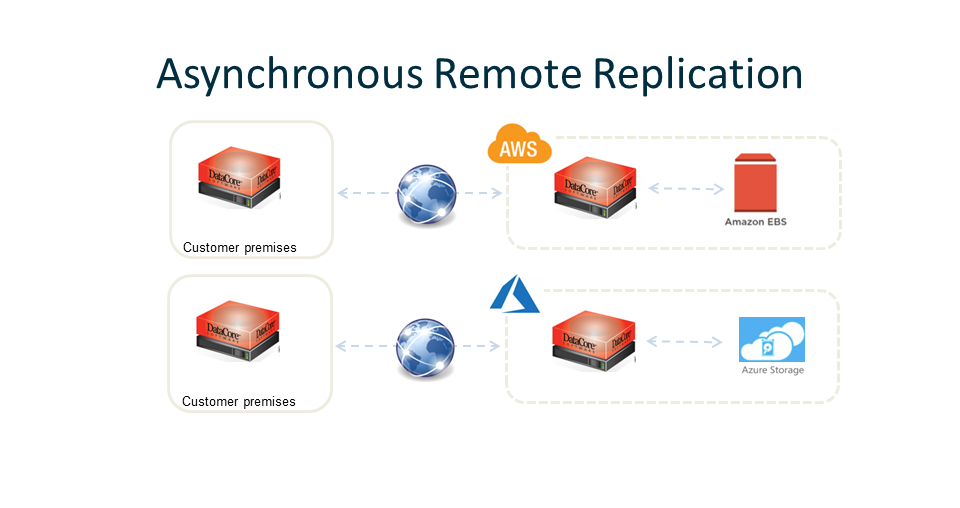
Asynchronous remote replication streams change data continuously to the remote site, where it can be used for disaster recovery. Critical data and applications are continuously replicated, asynchronously, to have a fallback if it comes to the worst-case scenario. The duplicated data becomes quickly accessible in the event that the production site becomes unavailable. Asynchronous mirroring provides the highest integrity and the most flexible disaster recovery service for all applications and business critical data.
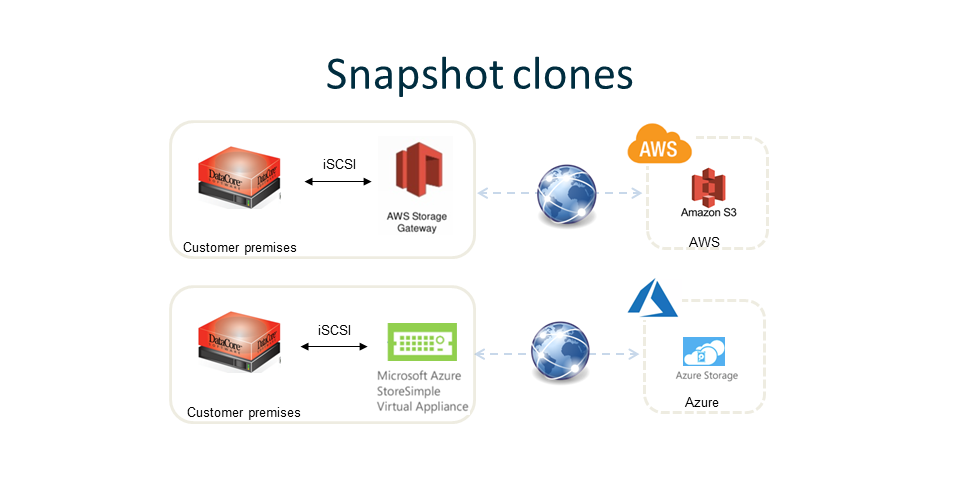
 The snapshot clone backup deploys a cloud gateway connector on-premises. Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure both offer such gateways. The use of Amazon S3 (and Azure equivalent) cloud storage provides for an economical alternative to on-premises alternatives.
The snapshot clone backup deploys a cloud gateway connector on-premises. Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure both offer such gateways. The use of Amazon S3 (and Azure equivalent) cloud storage provides for an economical alternative to on-premises alternatives.
All the elements exist to deploy either of the above configurations today. For an example, see the cloud integration page on our site.
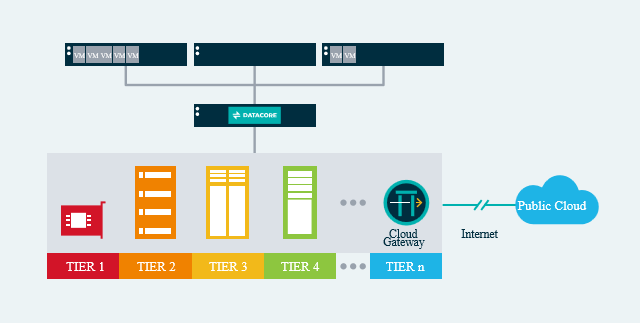
In summary, software-defined storage data services including asynchronous remote replication and snapshot clones, available now from DataCore Software, can make it much simpler for enterprises to utilize the cloud to efficiently roll out a secure remote replication site. It can also help enterprises more effectively achieve mission-critical business objectives such as efficient disaster recovery. In addition, enterprises with a diverse mix of storage brands or models can run software-defined storage on-premises to consolidate and unify data replication to the cloud for all storage assets versus dealing with the complexity and cost of implementing piecemeal vendor-by-vendor approaches.